Abstract
Many investors have significant long equity market exposure and seek effective portfolio protection. Several strategies for tail risk hedging have been proposed to provide downside protection in equity market sell-offs, notably a) increasing fixed income allocation, b) buying protective puts through the sale of out-of-the-money calls (collars), c) hedging using VIX futures, and d) allocating to Managed Futures or other alternative risk premia strategies. In this paper, we examine the popular strategies for tail risk hedging and highlight the cost-benefits of each.
摘要
许多投资者都有很长的股票市场风险并寻求有效的投资组合保护 已经提出了几种尾部风险对冲策略,以提供股票市场抛售的下行保护,特别是a)增加固定收益分配,b)通过出售价外看涨期权(领子)购买保护性看跌期权,c )使用VIX期货进行套期保值,以及d)分配管理期货或其他风险溢价策略。 在本文中,我们研究了尾部风险对冲的流行策略,并强调了每种策略的成本效益。
Keywords: Tail Risk; Hedging; Diversification; Trend Following
关键词:尾部风险;套期保值; 多样化; 趋势跟随
1. Introduction
In statistics “tails” are defined as the extremes of distribution(i.e., those outcomes that have a small probability of occurring).In finance, the term tail events typically refer to infrequent, outsized downside market moves such as those observed during the 2008 financial crisis. There is no broadly accepted definition of what constitutes a tail event, but consensus holds that we see moves larger than those expected by financial models, approximately every 3–5 years on average. In recent years equity markets have soared and investors are increasingly looking to have a hedge against their equity exposure. Because tail events are difficult to predict, and by their extreme nature can have a profound impact on a portfolio, protection from tail events can be a valuable component of a diverse portfolio.
1.简介
在统计中,“尾部”被定义为分布的极端(即那些发生概率很小的结果)。在金融领域,尾部事件一词通常指的是不常见的,超大的下行市场变动,例如2008年金融时期观察到的变化。 危机。 关于什么构成尾部事件没有广泛接受的定义,但一致认为我们认为变动大于金融模型预期的变动,大约平均每3 - 5年。 近年来,股票市场飙升,投资者越来越希望对冲其股票风险。 由于尾部事件很难预测,并且由于其极端性质会对投资组合产生深远影响,因此对尾部事件的保护可能是多样化投资组合的重要组成部分。
Tail Risk Hedging
Even supposedly diverse portfolios are often susceptible to the significant risk associated with a sustained fall in equities prices. Traditionally, investors have used the fixed income to offer some protection during equity bear markets. It has been observed that equities and bonds show a high negative correlation during times of exceedingly high volatility [Connolly et al. (2005)]. Therefore, increasing fixed income allocation in a portfolio has been advocated to help mitigate the downside exposure of equities in times of high market risk. There are potential pitfalls inherent in this strategy. For example, a classic 60-40 equities-bond portfolio effectively equates to over a 90-10 allocation in terms of realized risk with equities dominating bonds. As a result, the protection offered by the fixed income allocation may be less than anticipated. One way to address this is through the construction of a risk-parity portfolio where equities and bonds have equal risk allocations. Some market participants use options to try to mitigate tail risk.
尾部风险套期保值
即使是多样化的投资组合,也往往容易受到与股票价格持续下跌相关的重大风险的影响。传统上,投资者利用固定收益在股票熊市中提供一些保护。据观察,在波动性极高的时期,股票和债券显示出高度的负相关性[Connolly et al。 (2005)]。因此,提倡增加投资组合中的固定收益分配,以帮助减轻股市在高市场风险时的下行风险。这一战略存在潜在的陷阱。例如,一个典型的60-40股票债券投资组合实际上相当于在股票主导债券的已实现风险方面超过90-10。因此,固定收益分配提供的保护可能低于预期。解决这个问题的一种方法是建立风险平价投资组合,其中股票和债券具有相同的风险分配。一些市场参与者使用选项来尝试降低尾部风险。
For example, a traditional capital preservation strategy like a collar works by selling out of the money calls and using the premium to buy out of the money puts. This effectively sets a floor and ceiling to potential profit and loss from movements of the underlying asset.VIX Futures provide another volatility-based indirect hedging strategy. The VIX index tracks the volatility of S&P 500options and is commonly referred to as the “fear gauge” of equity markets. It is an aggregation of the implied volatilities of the puts and calls that expire approximately within a month’s time. Equity market sell-offs are typically accompanied by a spike in market volatility. For example, during the market uncertainty of2008, the VIX surged to historic highs over the course of two months as markets fell. By going long VIX futures contracts in an appropriate hedge ratio, one can hedge exposure to the underlying equity market. Commodity Trading Advisors (CTAs) attempt to capture trends in futures markets. CTAs tend to have a low correlation to equity assets, and as such, they can be used to mitigate risk in an equity-dominant portfolio. The directional nature of such funds can potentially lead to high returns in times of market stress.
例如,像Collar(领子期权组合)这样的传统资本保值策略就是通过卖出资金来电并使用溢价来买入资金。这有效地确定了标的资产变动带来的潜在利润和损失.VIX期货提供了另一种基于波动率的间接对冲策略。VIX指数跟踪标准普尔500指数的波动性,通常被称为股票市场的“恐惧指标”。它是看跌期权和看涨期权的隐含波动率的汇总,大约在一个月的时间内到期。股票市场抛售通常伴随着市场波动性的飙升。例如,在2008年的市场不确定性期间,由于市场下跌,VIX在两个月内飙升至历史高位。通过以适当的套期保值比率持有多头VIX期货合约,人们可以对冲相关股票市场。商品交易顾问(CTAs)试图捕捉期货市场的趋势。CTA往往与股权资产的相关性较低,因此,它们可用于降低股权主导投资组合的风险。这些基金的方向性可能会在市场压力时带来高回报。
2. Methodology
In this paper, we will evaluate various tail risk hedging strategies to measure their effectiveness. The base comparison case is a 60-40 portfolio with a 60% allocation to the S&P Total ReturnIndex (SPTR) and 40% allocation to the US Aggregate BondIndex (LBUSTRUU). The four strategies we consider are
1. Risk-Parity: a portfolio having equal risk allocation to SPTR and LBUSTRUU instead of 60-40 allocation of capital.
2. Collars: a portfolio replacing long exposure to S&P 500in the base portfolio with a 60% allocation to CLL Index(95-110 Collar) instead of SPTR.
3. VIX Futures: a portfolio where we hedge 10% of benchmark equity exposure at any given time by going long VIX futures.1
4. CTA: a portfolio with a 20% allocation to the 20% volatility targeted Barclay Hedge CTA Index.
2.方法论
在本文中,我们将评估各种尾部风险对冲策略来衡量其有效性。基本比较案例是60-40投资组合,标准普尔总回报指数(SPTR)分配60%,美国综合债券指数(LBUSTRUU)分配40%。我们考虑的四种策略是
1.风险平价:投资组合具有与SPTR和LBUSTRUU相等的风险分配,而不是60-40的资本分配。
2.领子期权组合:一个投资组合取代了标准普尔500指数在基础投资组合中的长期风险,其中60%分配给CLL指数(95-110领)而不是SPTR。
3. VIX期货:一种投资组合,我们通过持有多头VIX期货在任何特定时间对冲基准股票敞口的10%
4. CTA:对20%波动率分配20%的投资组合,目标是Barclay Hedge CTA指数。
1A hedge ratio is calculated based on rolling beta of VIX Futures to S&P 500.
3. Discussion
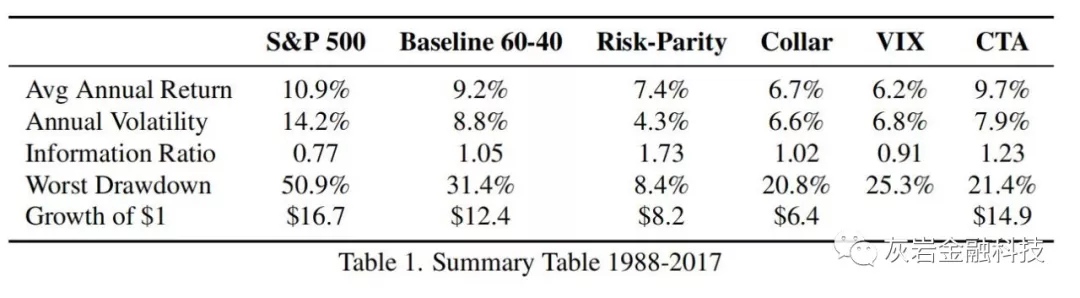
Table 1 compares the various hedging strategies starting in 1988. The benchmark 60-40 portfolio has a worst drawdown of 31.4%compared to 50.9% for the S&P 500, and an average annual return of 9.2% (historical drawdowns are plotted in Figure 1).In comparison, the risk-parity portfolio of stocks and bonds has the lowest drawdown but also reduces the average returns due to the much lower volatility of the fixed income allocation. It also has the highest Information Ratio (IR) among all the evaluate hedging strategies. However, the high IR of risk-parity can in part be explained by an unprecedented drop in bond yields over the 30year backtest period that is unlikely to be repeated in a rising rate environment. Increasing fixed income allocation to protect against equity sell-offs only works under the assumption that equities and bonds maintain their negative correlation. However, this has not been true historically for long periods of times [see GCMresearch note on equity-bond correlation]. Risk parity also makes use of leverage to deliver higher volatility, which can exacerbate drawdowns in periods of simultaneous bond and equity market sell-offs.
表1比较了1988年开始的各种套期保值策略。基准60-40投资组合的最低跌幅为31.4%,标准普尔500指数为50.9%,平均年回报率为9.2%(历史下跌幅度见图1)相比之下,由于固定收益分配的波动性低得多,股票和债券的风险平价投资组合的跌幅最低,但也降低了平均回报率。它在所有评估对冲策略中也具有最高的信息比率(IR)。然而,风险平价的高IR可以部分解释为30年后验期间债券收益率出现前所未有的下降,这在不断上升的利率环境中不太可能重演。增加固定收益分配以防止股权抛售只能在假设股票和债券保持负相关的情况下才有效。然而,这在历史上并非长期存在[见GCMresearch关于股票债券相关性的说明]。风险平价还利用杠杆来提供更高的波动性,这可能会加剧同时债券和股票市场抛售期间的亏损。
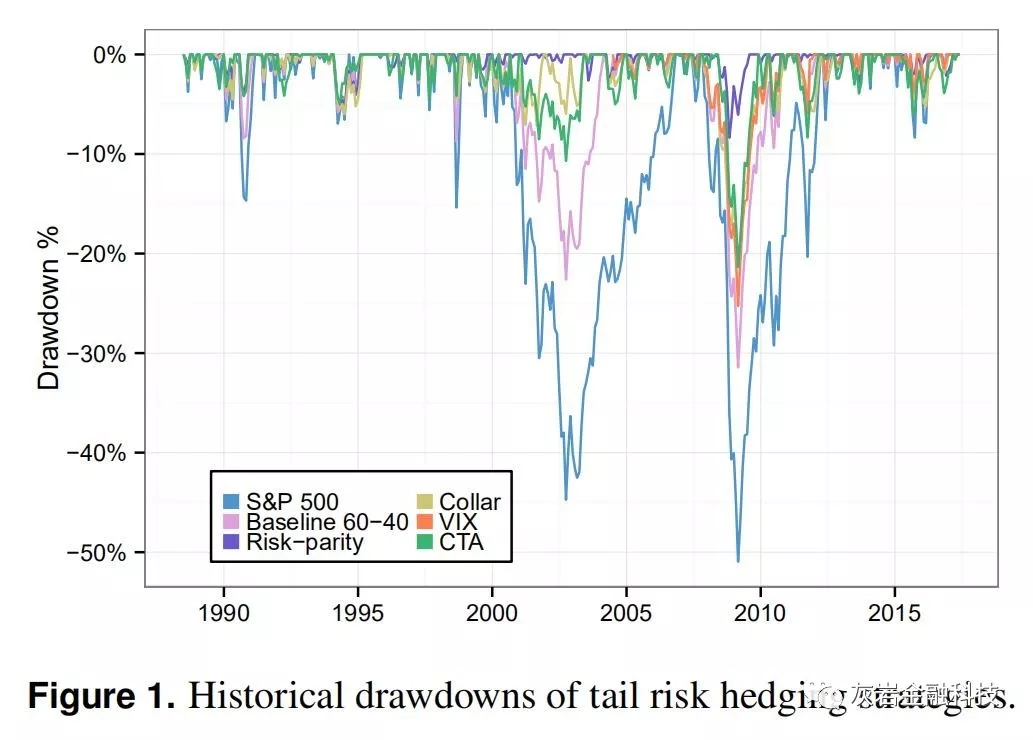
Figure 1. Historical drawdowns of tail risk hedging strategies. A collar hedging strategy has a similar IR as the 60-40 benchmark portfolio and a significantly lower worst drawdown of 20.8%; however, it results in significantly lower cumulative wealth. Buying collars eliminate much of the potential upside from equity rallies and this can be further compounded by the high transaction costs associated with trading options. Hedging with VIX futures2looks superficially similar to the collar hedging strategy. Compared to the benchmark portfolio it gives a lower IR albeit with a better drawdown profile. Some protection is afforded by the negative correlation between VIX futures and equities, but VIX futures are often in a state of contango and the negative roll yield associated with the hedge position can act as a drag on the portfolio. The CTA hedging strategy exhibits higher cumulative wealth and IR than does the benchmark, along with an improved drawdown profile. Historically CTAs have performed well during crisis periods for equities as they can take short positions in downward trending markets. Unlike some of the other hedging strategies described here, CTAs can also see significant positive returns when equity markets are doing well, and as a result, are less likely to detract from performance during strong periods for equities.
图1.尾部风险对冲策略的历史下降。领域对冲策略与60-40基准投资组合具有相似的IR,并且显着降低20.8%的最差跌幅;然而,它导致累积财富显着降低。购买领子期权组合消除了股票反弹的潜在上行空间,而且与交易期权相关的高交易成本可能进一步加剧这种情况。对VIX期货2进行套期保值表面看起来类似于领套期保值策略。与基准投资组合相比,它提供了更低的IR,尽管具有更好的下降轮廓。VIX期货与股票之间的负相关提供了一些保护,但VIX期货通常处于期货状态,与套期保值相关的负滚动收益率可能会拖累投资组合。CTA对冲策略显示出比基准更高的累积财富和IR,以及改善的缩减概况。历史上,CTA在股票危机期间表现良好,因为它们可以在下行趋势市场中做空头寸。与此处描述的其他一些对冲策略不同,当股票市场表现良好时,CTA也可以看到显着的正回报,因此在股票的强势时期内不太可能降低业绩。
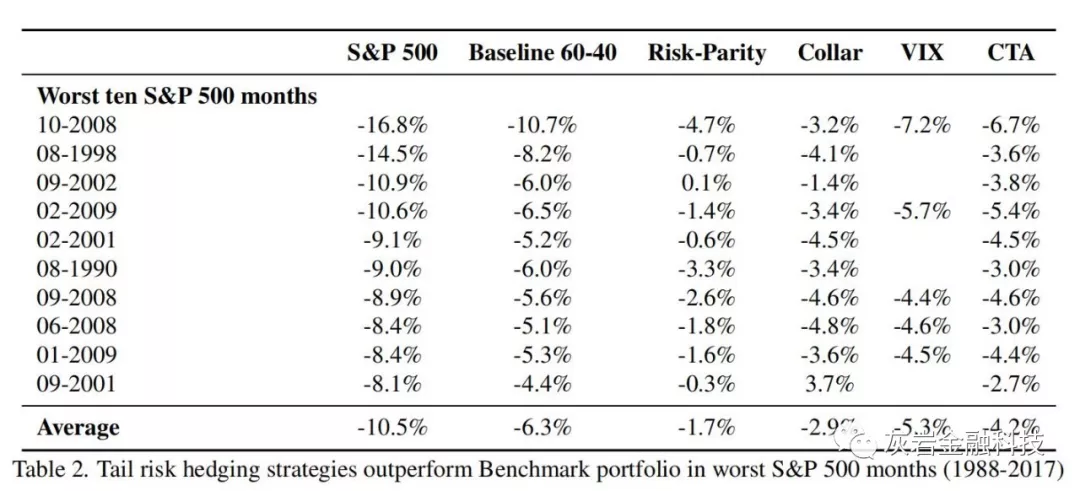
Table 2 examines the performance of tail risk hedging strategies in the ten worst S&P 500 months. We find that all of them outperformed the 60-40 benchmark in every single instance.
表2考察了标准普尔指数最差的10个月中尾部风险对冲策略的表现。我们发现它们在每一个实例中都优于60-40基准。
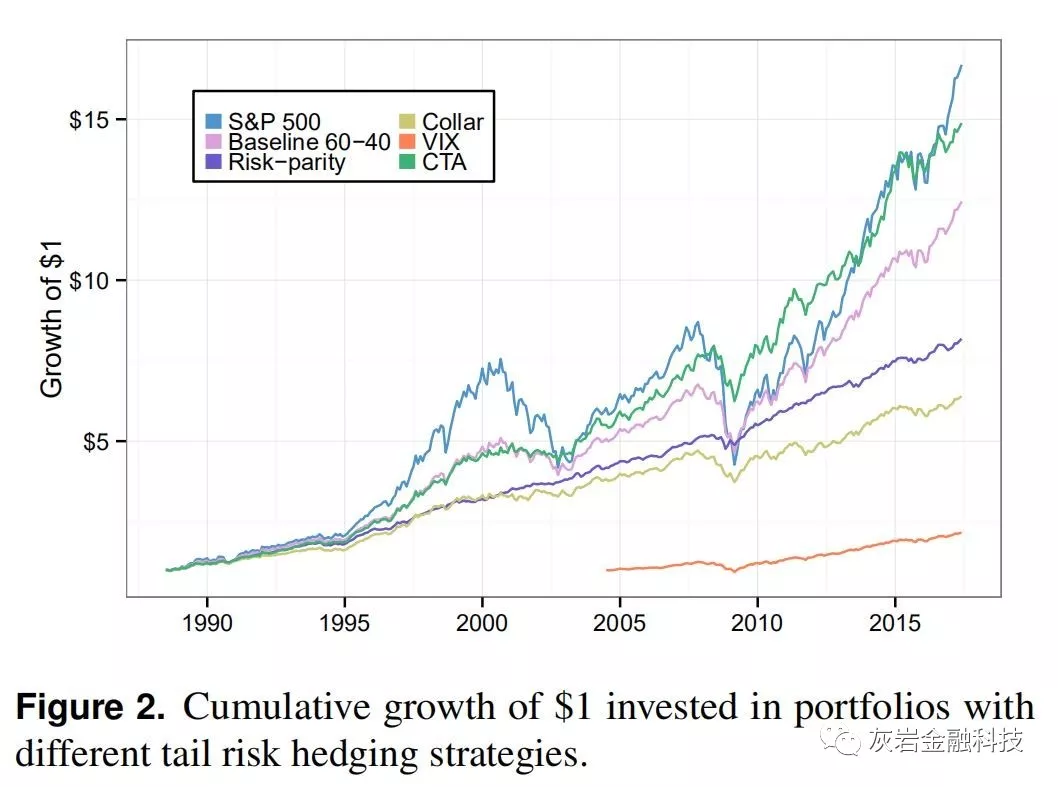
Charting cumulative growth of $1 in Figure 2 has the CTAhedged portfolio outperforming all other hedging strategies by a wide margin. CTA allocation is able to deliver high volatility in combination with uncorrelated alpha to give nearly the same total wealth as does the S&P 500. Direct hedging using options decisively gives the lowest returns out of all the strategies. The risk-parity portfolio can’t compensate enough for low volatility with its high IR and gives lower terminal wealth than does the benchmark
图2中累计增长1美元的图表显示,CTAhedged投资组合大幅超越所有其他对冲策略。CTA分配能够提供高波动性与不相关的α相结合,以提供与标准普尔500指数几乎相同的总财富。使用期权的直接套期保值决定性地给出了所有策略中的最低回报。 风险平价投资组合无法通过其高IR来弥补低波动性,并且提供比基准更低的终端财富
.4. Conclusion
In this paper we evaluated four tail risk hedging strategies –increasing fixed income allocation, direct hedging using options, VIX Futures, and CTAs. Increasing fixed income allocation to form a risk-parity portfolio has historically achieved a very high IR and good tail protection, but significantly lower terminal wealth. Volatility based hedging strategies have lower IR than the benchmark portfolio and realize lower volatility leading to lower cumulative growth. Finally, we find that CTAs provide a high-degree of tail protection, with higher IR and similar volatility to a60-40 benchmark.
4.结论
在本文中,我们评估了四种尾部风险对冲策略 - 增加固定收益分配,使用期权直接对冲,VIX期货和CTA。增加固定收益分配以形成风险平价投资组合历史上已经实现了非常高的IR和良好的尾部保护,但终端财富显着降低。基于波动率的对冲策略比基准投资组合具有更低的IR,并且实现更低的波动率,从而导致更低的累积增长。 最后,我们发现CTA提供高度的尾部保护,具有更高的IR和类似的波动性,达到60-40基准。
References
Connolly, Stivers, and Sun. Stock market uncertainty and the stock-bond return relation. The Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 40(1):161–194, 2005.
未经允许不得转载:美股开户者 » 长尾对冲(一)Tail Risk Hedging
 美股开户者
美股开户者